Malaria
Introduction
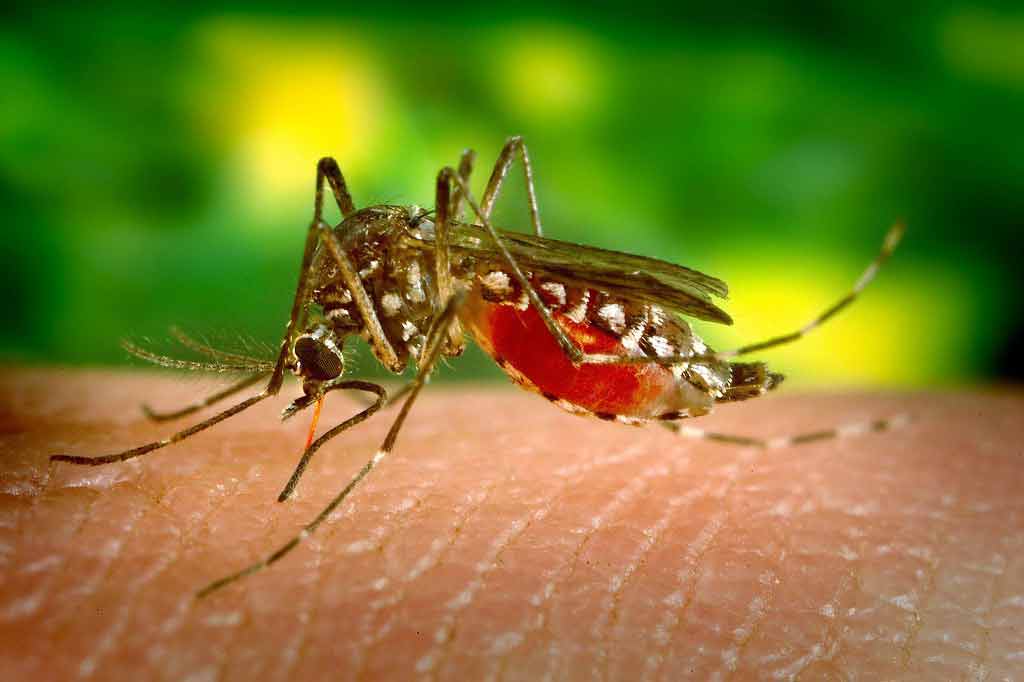
Malaria is a serious tropical disease spread by mosquitoes. If it isn't diagnosed and treated promptly, it can be fatal.
A single mosquito bite is all it takes for someone to become infected.
Symptoms of malaria
It's important to be aware of the symptoms of malaria if you're travelling to areas where there's a high risk of the disease. Symptoms include:
Symptoms usually appear between 7 and 18 days after becoming infected, but insome cases the symptoms may not appearfor up to a year, or occasionally even longer.
You should still seek medical help even if it's several weeks, months or a year after you return from travelling.
If there's a possibility you have malaria, a blood test will be carried out to confirm whether or not you're infected.
You should receive the results of your blood test on the same day. If you have malaria, treatment will be started straight away.
What causes malaria?
Malaria is caused by a type of parasite known as Plasmodium. There are many different types of Plasmodia parasites, but only five cause malaria in humans.
The Plasmodium parasite is mainly spread by female Anopheles mosquitoes, which mainly bite at dusk and at night. When an infected mosquito bites a human, it passes the parasites into the bloodstream.
Malaria can also be spread through blood transfusions and the sharing of needles, but this is very rare.
An easy way to remember is the ABCD approach to prevention:
- Awareness of risk find out whether you're at risk of getting malaria before travelling
- Bite prevention avoid mosquito bites by using insect repellent, covering your arms and legs, and using an insecticide-treated mosquito net
- Check whether you need to take malaria prevention tablets if you do, make sure you take the right antimalarial tablets at the right dose, and finish the course
- Diagnosis seek immediate medical advice if you develop malaria symptoms, as long as up to a year after you return from travelling
Speak to your GP if you're planning to visit an area where there's a malaria risk. It may be recommended that you take antimalarial tablets to prevent infection.
Treatment should be started as soon as the diagnosis has been confirmed.
Antimalarial medication is used to both treat and prevent malaria. Which type of medication is used and the length of treatment will depend on:
- the type of malaria
- the severity of your symptoms
- where you caught malaria
- whether you took an antimalarial to prevent malaria
- whether you're pregnant
In some cases, you may be prescribed emergency standby treatment for malaria before you travel. This is usually if there's a risk of you becoming infected with malaria while travelling in a remote area with little or no access to medical care.
It can be fatal if not treated promptly.
It can also cause serious complications, including:
- severe anaemia where red blood cells are unable to carry enough oxygen around the body, leading to drowsiness and weakness
- cerebral malaria in rare cases, the small blood vessels leading to the brain can become blocked, causing seizures, brain damage and coma
The effects of malaria are usually more severe in pregnant women, babies, young children and the elderly. Pregnant women in particular are usually advised not to travel to malaria risk areas.
Introduction
Malaria is a serious tropical disease spread by mosquitoes. If it is not diagnosed and treated promptly, it can be fatal. A single mosquito bite is all it takes for someone to become infected. It's also important to be aware of the symptoms of malaria.
Symptoms
Symptoms of malaria can develop as quickly as seven days after you are bitten by an infected mosquito. Typically, the time between being infected an dwhen symptoms start (incubation period) is 7 to 18 days.
Causes
Malaria is caused by the Plasmodium parasite. The parasite can be spread to humans through the bites of infected mosquitoes. There are many different types of plasmodium parasite, but only five types cause malaria in humans.
Antimalarial medication
Antimalarial medication is used to prevent and treat malaria. You should always consider taking antimalarial medicine when travelling to areas where there's a risk of malaria.
Complications
Malaria is a serious illness that can be fatal if not diagnosed and treated quickly, particularly in pregnant women, babies, young children and the elderly. The Plasmodium falciparum parasite causes the most severe malaria symptoms and most deaths.
Prevention
There is a significant risk of getting malaria if you travel to an affected area. It is therefore very important that you take precautions to prevent it. Malaria can often be avoided using the ABCD approach to prevention.
'I was so weak, I couldn't even pick up a glass'
Unlike many travellers, Alex Beard was careful to take precautions against getting bitten by a malaria-carrying mosquito.







 Subscribe
Subscribe Ask the doctor
Ask the doctor Rate this article
Rate this article Find products
Find products